Bitcoin first surfaced in 2008 through a published paper “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” by an individual using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Given the nature of how Bitcoin started and the complexity of cryptocurrencies, a mysterious cloud still surrounds Bitcoin. Let’s clear the air.
side note: Worldline currently does not support Bitcoin or any cryptocurrency.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized form of currency. Decentralized means that the currency trades directly from person-to-person, compared to current electronic transfers where a bank or a clearing house acts as a middleman.
Bitcoin is also open-sourced, which means that anyone can review the code and create a modified version. This has made it popular among the developer community who values transparency and collaboration.
The Bitcoin currency
The Bitcoin currency itself is similar to stocks. There will only ever be 21 million bitcoin created but at the moment, 1 bitcoin can be broken down by 8 decimals or to 0.000,000,01 bitcoin with the possibility of it being broken down even further.
Did you know? When you are talking about the network it’s Bitcoin, when you are talking about the currency it’s bitcoin.
The value of Bitcoin is driven by supply and demand – the more demand for Bitcoin, the higher the price while the lower the demand, the lower the price. At the date of publishing this blog, $1 bitcoin was equal to $2,297.59 CAD.
Four ways you can get bitcoin.
The first way is through a Bitcoin exchange where you can purchase them using your currency, again similar to the stock market. You would then use a mobile wallet app or computer program to send and receive bitcoin.
You can also trade cash with someone in-person using services, like LocalBitcoins, that help people connect locally. You could also sell a service or good and accept bitcoin as payment.
The final way to obtain bitcoin is to “mine”. For Bitcoin to work as a currency it needs a lot of specialized computer power to secure the network. Remember, Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer network so this computing power comes from its users. To mine you must purchase specialized hardware designed specifically for Bitcoin. When you contribute to the network with this hardware, you earn Bitcoin.
The bitcoin transaction life cycle
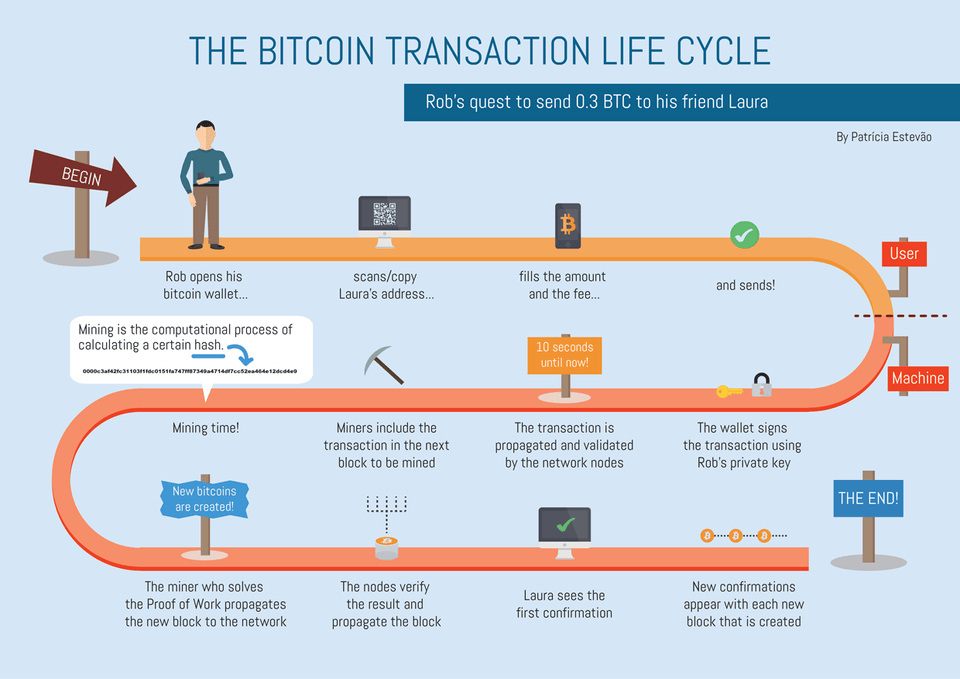
How does Bitcoin work
For the merchant or consumer, sending and receiving bitcoin is relatively easy. It’s what happens in the back end that can be confusing.
Each transaction ever made using bitcoin is recorded in a public ledger called the blockchain. Anyone can access the blockchain, which allows the network to verify the number of bitcoin associated with an individual’s private key.
Once the network verifies that the bitcoin are available, the transaction gets added to the next batch in the mining workload. Once the mining is complete, the transaction gets added to the blockchain and the transaction is complete.
There are many advantages and disadvantages to Bitcoin, which we encourage you to explore further.
